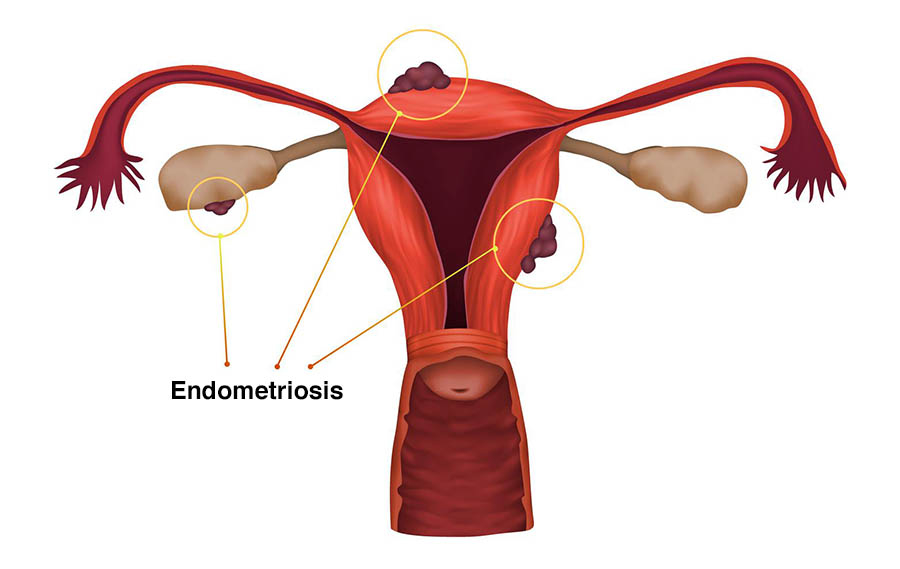
The diagnosis of endometriosis is often difficult and this is secondary to a number of factors: Lack of awareness, incomplete understanding of the disease, heterogeneity of endometriosis, and co-existing diseases make the diagnosis complex. The mean delay from first symptom to diagnosis of endometriosis is around 8 years1. Many symptoms may first appear during adolescence and are often ignored as being ‘’normal’’. A detailed clinical history and examination are of paramount importance; however, they are rarely enough on their own. Before going further, we have to, at this point, remember the 3 types of the disease2.
- Eπιφανειακές περιτοναικες βλαβες: παραδοσιακά, αυτός ο τύπος της νόσου διαγιγνώσκεται με τη λαπαροσκοπική χειρουργική (3). Αυτό επιτρέπει στον γυναικολόγο να δει ξεκάθαρα τις βλάβες της ενδομητρίωσης κι, εφόσον μπορεί, να τις αφαιρέσει ταυτόχρονα. Μιας κι οι βλάβες αυτές είναι επιφανειακές, παραμένει τεχνικά πιο δύσκολο να διαγνωστούν με μη επεμβατικές μεθόδους (4). Αν και μη επεμβατικές τεχνικές έχουν περιγραφεί στη διάγνωση αυτού του τύπου της νόσου (5), η χρήση τους δεν είναι ακόμη ευρέως διαδεδομένη. Η αναστολή της ωοθυλακιορρηξίας με χρήση ορμονών είναι μια χρήσιμη δοκιμασία ώστε να μειωθούν οι άσκοπες διαγνωστικές λαπαροσκοπήσεις (λαπαροσκοπήσεις με σκοπό τη διάγνωση ή μη της νόσου).
- Ενδομητριώματα: Αυτός ο τύπος νόσου έχει χαρακτηριστική εικόνα, τόσο στον διακολπικό υπέρηχο (transvaginal ultrasound) όσο και στη Μαγνητική Τομογραφία (MRI). Μιας κι ο υπέρηχος κοστίζει λιγότερο από τη Μαγνητική Τομογραφία, είναι λογικό να αποτελεί την πιο συνήθη μέθοδο απεικόνισης για αυτόν τον τύπο της νόσου.
- Eν τω βάθει μορφή: Κι αυτός ο τύπος της νόσου μπορεί να διαγνωστεί με μη επεμβατικές μεθόδους. Υπάρχουν διαφορετικές απόψεις σχετικά με το αν η Μαγνητική Τομογραφία υπερτερεί ή όχι του διακολπικού υπερήχου (6-10). Πρέπει, επίσης, να ληφθεί υπόψη το πού βρίσκεται η νόσος αλλά κι η εμπειρία του/ της ιατρού που πραγματοποιεί την εξέταση (11). 'Eχει, επίσης, αποδειχτεί πως ο ενδελεχής υπέρηχος για την διάγνωση της ενδομητρίωσης παίρνει σημαντικά περισσότερο χρόνο από τον συμβατικό γυναικολογικό υπέρηχο (12). Τόσο ο υπέρηχος όσο κι η Μαγνητική Τομογραφία είναι, επίσης, αποτελεσματικά στη διάγνωση και της αδενομύωσης (παρουσία ενδομητρίου εντός του μυϊκού τοιχώματος της μήτρας) που συχνά συνυπάρχει με την ενδομητρίωση.
Aξίζει, συντόμως, να σημειωθεί πως υπάρχουν πρωτόκολλα για τη συστηματική περιγραφή (13), καθώς και τη σταδιοποίηση της νόσου (14), με τη χρήση υπερήχου. H αναλυτική περιγραφή τους δεν αποτελεί το αντικείμενο του παρόντος κειμένου.
Η χρήση ''βιοδεικτών'' (biomarkers) στο αίμα και τα ούρα ασθενών με σκοπό την διάγνωση της ενδομητρίωσης έχει μελετηθεί εκτενώς, ωστόσο, προς το παρόν, δεν είναι σε θέση να αντικαταστήσει τις παραδοσιακές μεθόδους διάγνωσης που αναφέρθηκαν παραπάνω15-17.
Εν κατακλείδι, το πρόβλημα ξεκινά με την καθυστέρηση στη διάγνωση της νόσου [70% των εφήβων κοριτσιών με πυελικό πόνο θα διαγνωστούν αργότερα με ενδομητρίωση].Η έγκαιρη κι έγκυρη διάγνωση μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε έγκαιρη και κατάλληλη μέθοδο αντιμετώπισης.
Αναφορές:
- Arruda MS, Petta CA, Abrão MS, Benetti‐Pinto CL. Time elapsed from onset of symptoms to diagnosis of endometriosis in a cohort study of Brazilian women. Hum Reprod 2003;18(4):756-759.
- Brosens I. Diagnosis of endometriosis. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 1997;15(3):229-33
- Brosens I, Puttemans P, Campo R, Gordts S, Kinkel K. Diagnosis of endometriosis: pelvic endoscopy and imaging techniques. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004 Apr;18(2):285-303.
- Leonardi M, Robledo KP, Espada M, Vanza K, Condous G. SonoPODography: A new diagnostic technique for visualizing superficial endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020 Nov;254:124-131.
- Indrielle-Kelly T, Frühauf F, Fanta M, Burgetova A, Lavu D, Dundr P, Cibula D, Fischerova D. Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasound and MRI in the Mapping of Deep Pelvic Endometriosis Using the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) Consensus. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jan 30;2020:3583989
- Abrao MS, Gonçalves MO, Dias JA Jr, Podgaec S, Chamie LP, Blasbalg R. Comparison between clinical examination, transvaginal sonography and magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of deep endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2007 Dec;22(12):3092-7.
- Guerriero S, Saba L, Pascual MA, Ajossa S, Rodriguez I, Mais V, Alcazar JL. Transvaginal ultrasound vs magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing deep infiltrating endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2018 May;51(5):586-595.
- Gerges B, Li W, Leonardi M, Mol BW, Condous G. Optimal imaging modality for detection of rectosigmoid deep endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Aug;58(2):190-200.
- Gerges B, Li W, Leonardi M, Mol BW, Condous G. Meta-analysis and systematic review to determine the optimal imaging modality for the detection of uterosacral ligaments/torus uterinus, rectovaginal septum and vaginal deep endometriosis. Hum Reprod Open. 2021 Nov 4;2021(4):hoab041.
- Scioscia M, Virgilio BA, Laganà AS, et al. Differential Diagnosis of Endometriosis by Ultrasound: A Rising Challenge. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(10):848.
- Deslandes A, Parange N, Childs JT, Osborne B, Panuccio C, Croft A, Bezak E. How long does a transvaginal ultrasound examination for endometriosis take in comparison to a routine transvaginal ultrasound examination? Australas J Ultrasound Med. 2021 Dec 5;25(1):20-27.
- Guerriero S, Condous G, van den Bosch T, Valentin L, Leone FP, Van Schoubroeck D, Exacoustos C, Installé AJ, Martins WP, Abrao MS, Hudelist G, Bazot M, Alcazar JL, Gonçalves MO, Pascual MA, Ajossa S, Savelli L, Dunham R, Reid S, Menakaya U, Bourne T, Ferrero S, Leon M, Bignardi T, Holland T, Jurkovic D, Benacerraf B, Osuga Y, Somigliana E, Timmerman D. Systematic approach to sonographic evaluation of the pelvis in women with suspected endometriosis, including terms, definitions and measurements: a consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;48(3):318-32.
- Keckstein J, Saridogan E, Ulrich UA, Sillem M, Oppelt P, Schweppe KW, Krentel H, Janschek E, Exacoustos C, Malzoni M, Mueller M, Roman H, Condous G, Forman A, Jansen FW, Bokor A, Simedrea V, Hudelist G. The #Enzian classification: A comprehensive non-invasive and surgical description system for endometriosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021 Jul;100(7):1165-1175.
- Nisenblat V, Bossuyt PM, Shaikh R, Farquhar C, Jordan V, Scheffers CS, Mol BW, Johnson N, Hull ML. Blood biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 1;2016(5):CD012179.
- Liu E, Nisenblat V, Farquhar C, Fraser I, Bossuyt PM, Johnson N, Hull ML. Urinary biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 23;2015(12):CD012019. doi: 10.1002/14651858.
- Nisenblat V, Prentice L, Bossuyt PM, Farquhar C, Hull ML, Johnson N. Combination of the non-invasive tests for the diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 13;7(7):CD012281. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012281.
- Yeung P Jr, Sinervo K, Winer W, Albee RB Jr. Complete laparoscopic excision of endometriosis in teenagers: is postoperative hormonal suppression necessary? Fertil Steril. 2011 May;95(6):1909-12.