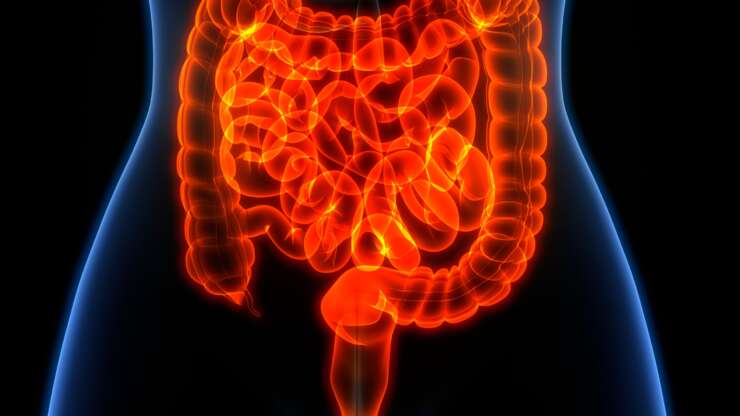
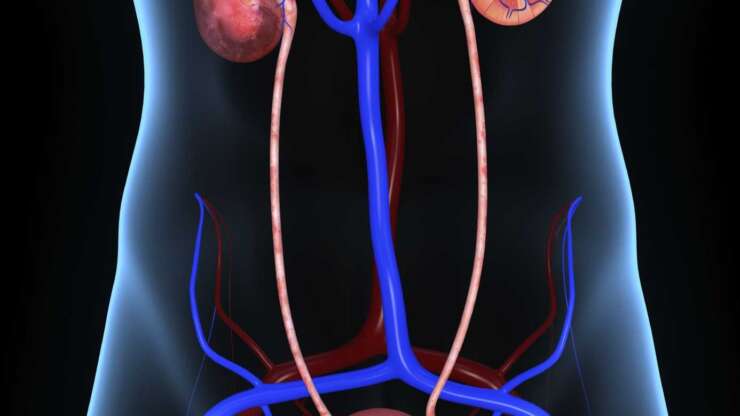
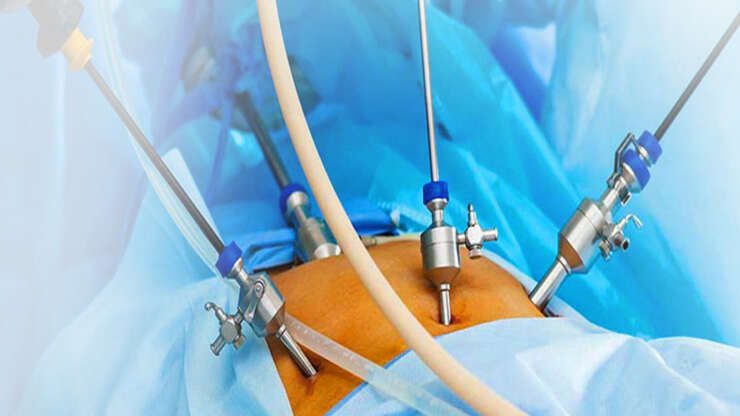
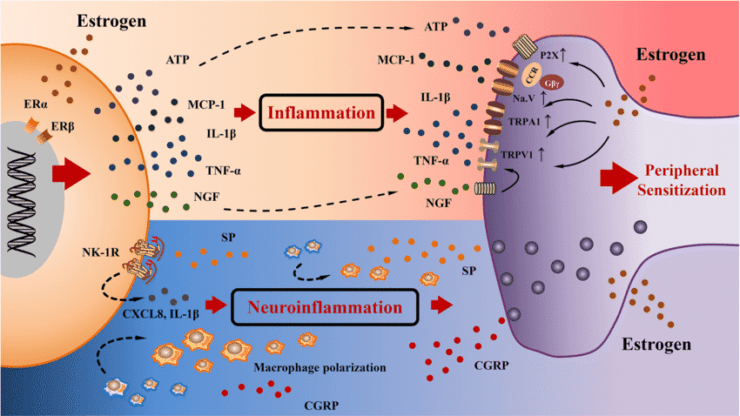
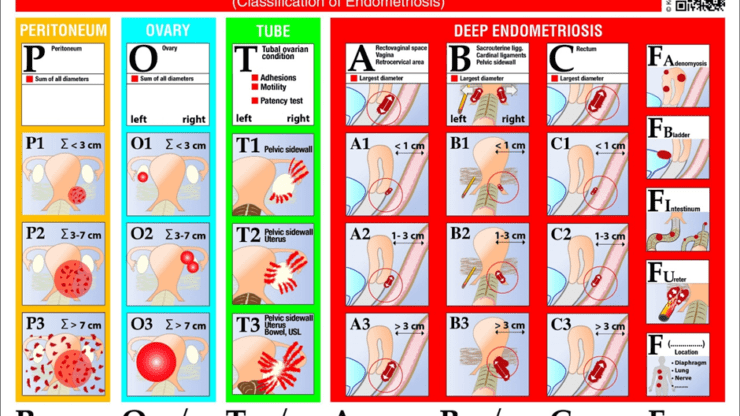
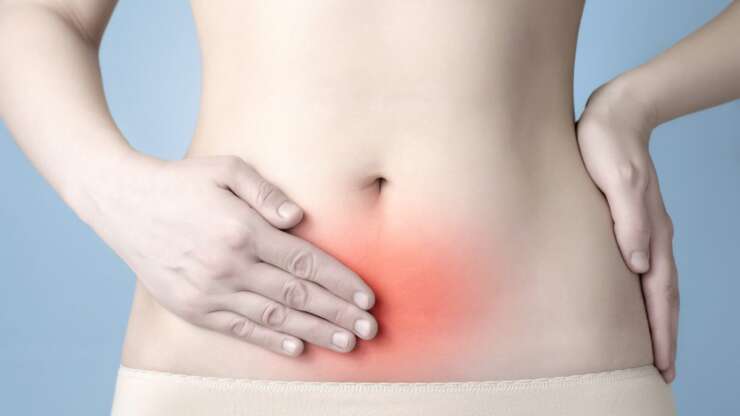
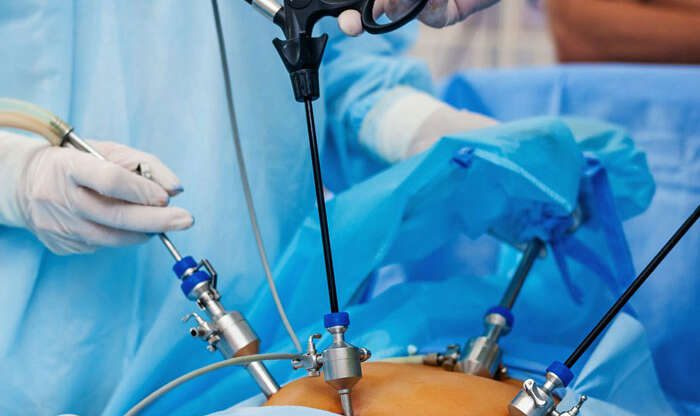
Endometriosis of the gastrointestinal system accounts for 5 to 12% of deep endometriosis cases1. 90% infiltrates the rectum and the sigmoid (large bowel)2. In most cases, the patients present with severe symptoms, such as the following: dyschezia (pain on opening the bowels), haematochezia (blood in the stools), bloating and change between constipation and diarrhoea. Those symptoms are, often, more intense…